Thoracic Strain: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
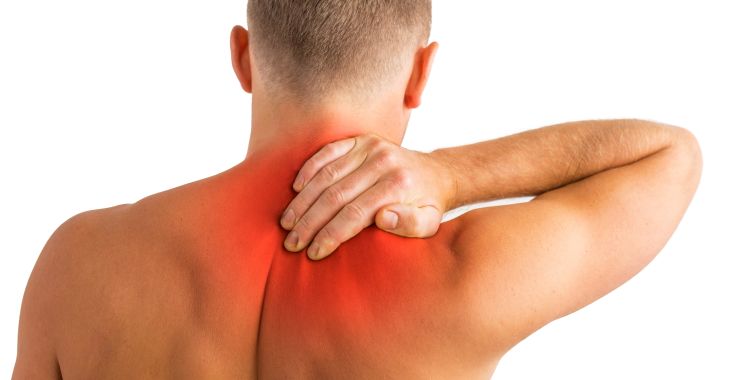
The midback is called the thoracic region, which extends from the base of the neck down to the bottom of the ribcage. When muscles in this region are torn from overexertion, accidents or repetitive motion, it is called a thoracic strain. If you have thoracic back pain, it may be a thoracic strain injury causing your discomfort.
What Causes a Thoracic Strain?
There are multiple muscles and tendons across the back that are essential for lifting, bending and using your arms. A thoracic strain is caused by injury to these tissues. Whenever fibers in the muscles are torn, it is called a strain. A thoracic sprain is similar, but involves injury to the thoracic ligaments. Some causes of thoracic strains include:
- Trauma to the back – falls, vehicle accidents
- Repetitive movements – sports or workplace injuries
- Overexertion when lifting
While thoracic spine injuries can also cause thoracic back pain, they are less common. The thoracic spine is less susceptible to herniated discs and other common spinal injuries in the cervical and lumbar spine. It is more common for a thoracic strain to muscles or tendons to cause back pain than a thoracic spinal injury.
Symptoms of Thoracic Strain Injuries
If you experience a thoracic sprain or strain, you will have symptoms that will alert you to your injury. The symptoms may occur at the time of the injury or worsen over time. The extent of your symptoms may depend on the severity of your muscle strain. Symptoms include:
- Thoracic back pain (midback between the neck and lower ribcage)
- A popping sensation in the midback
- Swelling and tenderness in the midback
- Limited range of motion when bending or lifting
- Pain when using or moving the back
- Midback is warm or red in affected area
If you have symptoms of a thoracic strain, you may need to rest or receive treatment. While some strains can heal on their own, others may require medical treatment. To avoid further aggravation of the injured muscles, avoid movements that result in thoracic back pain.
Treatment for Thoracic Muscle Injuries
Most thoracic tendon or muscle strains are mild and can be treated with conservative methods. Avoiding stress on the midback is recommended, resting and allowing the muscles or tendons to heal. To relieve discomfort, OTC anti-inflammatory pain medications can be used, along with ice.
When a few days of rest, ice and OTC medications do not relieve thoracic back pain, it may be time to see a doctor. Moderate to severe strains in the midback may require imaging and further diagnosis to ensure there is not injury to the spine. Treatment for moderate to severe thoracic strains include:
- Steroid injections to relieve inflammation and swelling
- Back brace to support the injured muscles and prevent further damage
- Pain medications to relieve discomfort
- Trigger point injections
- Prolotherapy
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy
- Physical therapy
Thoracic muscle or tendon strains rarely require surgery. Treatment usually revolves around allowing the torn tissue to repair itself, with exercises used to strengthen the muscles and tendons as they heal. Mild cases can resolve in a week or two, while more severe strains can require several weeks or longer of treatment.
- Prevention of Thoracic Sprains and Strains
- While some thoracic strains caused by trauma cannot be prevented, you can help protect your back from overexertion or repetitive strain. Some of the measures you can take to prevent midback injuries include the following.
- Strengthening Exercises
- Strengthening the back muscles is important – your doctor or physical therapist can recommend exercises to strengthen muscles in your thoracic region. Strengthening the muscles in your lower back and your abdomen can also help support the thoracic region.
- Stretching and Warming Up
- Warming up your muscles before beginning your work day or engaging in sports that require back movement can help prevent strains and sprains. Stretching and beginning with light exercise can protect muscles from sudden tears.
- Using Correct Lifting Techniques
- “Lift with your legs, not your back” is the common mantra for preventing back injuries. Bending the knees and keeping your back upright when lifting can limit strain on the back muscles and spine. Use your legs to lift whenever possible.
- Practice Good Posture
- Your posture is important for limiting strain on your back. Stand and sit up straight, with your head upright and your shoulders back. This will put less stress on your thoracic region.
- Use a Back Brace
- If you have a muscle strain or ligament sprain, use a back brace to help support your spine and musculoskeletal system while it heals.
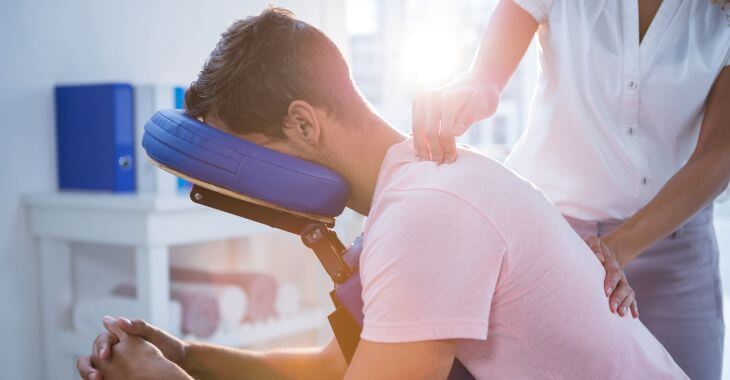
If you experience thoracic back pain, you may have injured the muscles in the midback region. If your symptoms are severe, visit your doctor for a diagnosis. You may have a thoracic strain injury that requires treatment to relieve your pain.
The information provided on this website, including text, graphics, images, and other materials, is intended solely for informational purposes and should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
)