Laser Therapy for Vascular Birthmarks
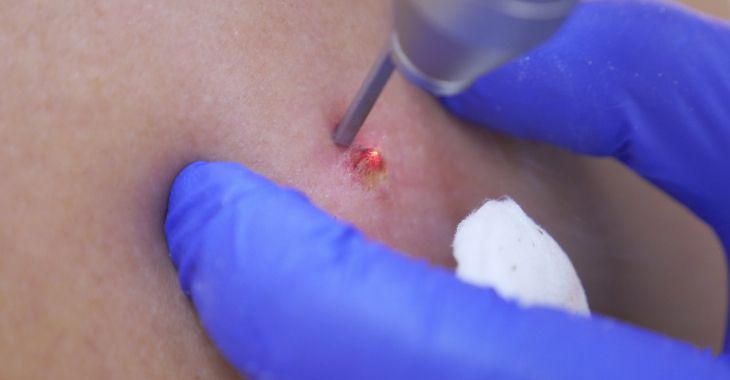
Many vascular birthmarks are located on the head, neck and upper body, making them very noticeable. For those that do not fade in early childhood, laser therapy can be an option to reduce the appearance of these red, blue or purple birthmarks. Both pulsed-dye lasers and YAG lasers can be used, depending on the type of birthmark. This can be a non-invasive option to improve the appearance of the skin and fade away a noticeable birthmark for aesthetic purposes.
Pulsed-Dye Laser Therapy
For strawberry, red or port-wine birthmarks that are flat, pulsed-dye lasers are often the best option for treatment. This treatment targets the surface blood vessels or spider veins that cause the reddish color. The laser can remove some surface blood vessels and fade the reddish color. When completed on younger patients, the results can be excellent, fading the birthmark and retaining the skin health.
YAG Laser Therapy
YAG laser therapy can be a better treatment for fading or reducing the size of blue or purple birthmarks. The crystal laser targets the melanin in the skin that causes the discoloration. After the treatment, the birthmark darkens temporarily, then the darker skin cells slough away. Each YAG laser treatment can fade the birthmark further, while preserving the texture of the skin.
Most patients receiving birthmark removal are children, but laser therapy can be used on birthmarks at any age. If you or your child has a disfiguring birthmark you want removed or faded, laser therapy may be an option. Laser therapy can be done during an office visit and is usually has minimal discomfort. Contact a vascular birthmark specialist to learn more about laser therapy and other birthmark treatment options.
Posted on behalf of:
The Vascular Birthmark Center Los Angeles
435 N. Bedford Drive, Suite 203
Beverly Hills, CA 90210
(610)301-4522
The information provided on this website, including text, graphics, images, and other materials, is intended solely for informational purposes and should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
)