Risk Factors for Varicose Veins
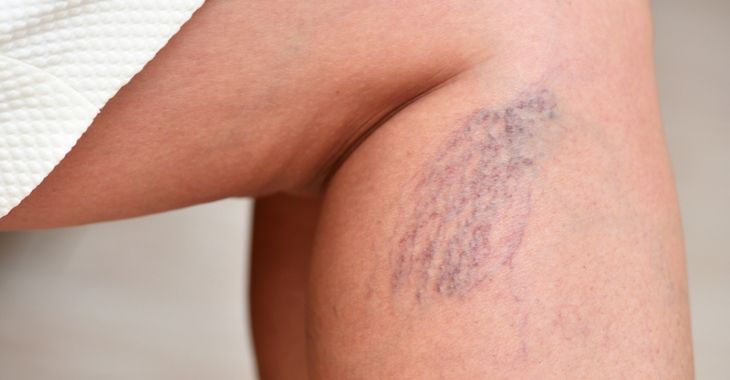
Pronounced, enlarged veins in the legs and feet are a common occurrence. Varicose veins occur in up to 30% of people and anyone can be affected with these large veins. This condition occurs when the valves in the vein are not working properly, allowing the blood to backflow or pool, stretching and twisting the vein. Beyond the appearance and pain, varicose veins can increase the risk for blood clots, DVT and pulmonary embolism. While anyone can have varicose veins, there are risk factors that are linked to creating these twisted, enlarged veins.
Woman are at Higher Risk
Women are more likely to get varicose veins. Estrogen and female hormones can put women at higher risk, as can other factors that only women experience. Pregnancy and some birth control pills/methods that contain hormones can increase the risk for varicose veins.
Weight and Age
Obesity can increase the risk for varicose veins, putting more pressure on the vein walls that can lead to damage. Varicose veins are also more common as you get older, especially if you are over forty. While you cannot stop aging, you can lose weight and be aware of other risk factors.
Vein Stress and Medical History
Jobs that require you to stand or sit for long periods can both put you at higher risk for varicose veins. Also, traumatic injuries to the veins can increase your risk. Genetics can also be a factor as can a history of blood clots.
You can reduce your risk of varicose veins by avoiding some of these impacting factors, but sometimes varicose veins cannot be avoided. If you acquire varicose veins, visit a vascular specialist to seek treatment to reduce the possibility of health complications and discomfort from these dysfunctional, large veins.
Posted on behalf of:
Alan Benvenisty, MD
1090 Amsterdam Avenue
New York, NY 10025
212-523-4706
The information provided on this website, including text, graphics, images, and other materials, is intended solely for informational purposes and should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.

)