Surgical Repair for Droopy Eyes

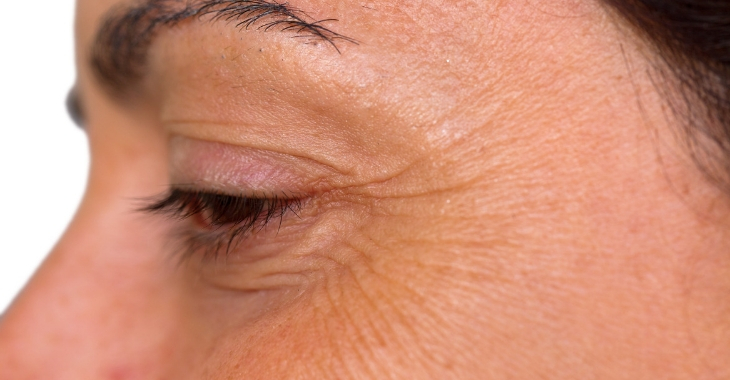
When the upper eyelid does not open completely, the eyes look tired. Just a tiny droop can change the overall appearance of the eyes and face. A droopy eyelid is a condition called ptosis, which can be caused by ruptured tendons in the eyelid (acquired ptosis) or it can be congenital. Not only can this condition make a person look tired, older or “lazy”, it can interfere with vision. For those with acquired ptosis, surgical repair can improve the function and appearance of droopy upper eyelids.
Surgical Treatment for Acquired Ptosis
Years of use and strain on the upper lid tendons can cause acquired ptosis. As the eyelid droops, more effort is needed to keep the eyes open, which can cause headaches and other discomfort. Correcting this issue can reduce strain, improve vision and alter the appearance of tired eyes. Surgery is required, which is best performed by an oculoplastic surgeon.
During this procedure, an incision is made at the crease on the affected upper eyelid. Patients may have one or both eyelids affected by acquired ptosis. The eyelid is elevated during the surgery, making it easier to fully open eyes. Patients with this procedure may notice they have fewer headaches and less fatigue from eye strain. Plus, they will look more energetic and youthful without their droopy eyes, which can help them feel more confident and attractive.
Those who have been told they look tired due to droopy eyes or have discomfort from acquired ptosis should seek a consultation with a oculoplastic surgeon, an ophthalmologist that specializes in plastic and reconstructive eye surgeries. With surgery, patients can look and feel more energetic when their acquired ptosis is corrected.
Posted on behalf of:
Kami Parsa, M.D.
Oculoplastic Surgery
465 N Roxbury Dr. Suite 1011
Beverly Hills, CA 90210
(310) 777-8880
The information provided on this website, including text, graphics, images, and other materials, is intended solely for informational purposes and should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
)