When Should a Lipoma be Removed?
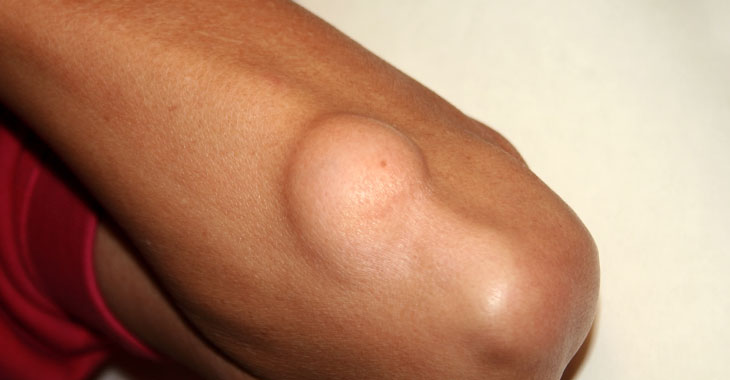
A lipoma is a benign, fatty tumor that grows underneath the skin. Most lipomas are small and painless, often located on the torso, neck, upper thighs, upper arms and armpits. It is not known exactly what causes these growths but they are usually inherited through the person’s genes. About 1% of the population will have at least one lipoma in their lifetime, many choosing to live with the small skin lump. However, there are situations when it may be best to have it removed.
Here are common reasons to pursue lipoma removal from a dermatologist:
- While lipomas are normally painless, they can press on a nerve, causing discomfort. If a lipoma is painful, have it removed.
- Depending on where a lipoma is located, it may cause friction or rubbing that can be uncomfortable. For example, lipomas on the torso can run against a waist band. If this occurs, it may be best to have the tumor removed.
- Unusual growth. If a lipoma suddenly begins growing or is quickly increasing in size, it should be removed for possible biopsy. While cancer is very rare, it is important to rule it out when there is unusual growth.
- Lipomas that are in visible areas may be aesthetically unappealing. Many people choose to have their lipomas removed for aesthetic reasons.
Lipoma removal Atlanta
If you have a lipoma that you want removed, call your local dermatology clinic for a consultation. Most lipoma treatment services are done as an outpatient surgery or even right in the doctor’s office. An experienced dermatologist can go over your options for treatment, including removal if your lipoma is causing you pain, discomfort or embarrassment.
Posted on behalf of:
Medical Dermatology Specialists
5730 Glenridge Drive, Suite T-100
Atlanta GA 30328
(404) 939-9220
The information provided on this website, including text, graphics, images, and other materials, is intended solely for informational purposes and should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.

)