Kybella Injections or Liposuction for a Double Chin?
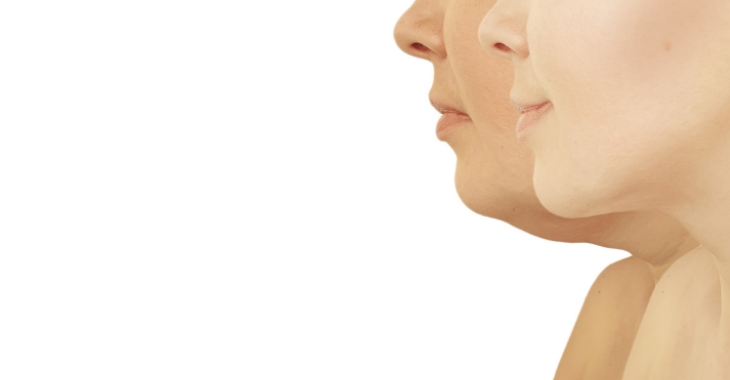
If you have decided it is time to find a solution to slim your double chin, you have two main cosmetic options available. Kybella injections are a non-invasive treatment that can decrease chin fat, while liposuction is a surgical procedure that can remove the fat causing a double chin. Both can be effective for creating a more defined facial appearance – here is a breakdown on the difference between the two treatments to help you decide which is right for you.
Kybella Injections
Kybella injections use a synthetic form of a bio-acid that destroys fat cells. When injected into chin fat, the fat cells disintegrate and are reabsorbed by the body. Several injections are used in each treatment, usually spaced about one month apart until the desired result is accomplished over 2-3 treatments. People using Kybella injections have gradual, seemingly natural, results without needing invasive surgery or downtime after the procedures.
Liposuction
If you want your chin fat removed in one procedure, consider liposuction. A small, discrete incision is made under the chin to access the fat pockets. Liposuction uses suction and surgical tools to remove the fat under the skin. This is an outpatient procedure and minimal downtime is required. There can be some bruising, draining and swelling expected during recovery. Liposuction can offer quicker results than Kybella, with a more defined chin noticeable once the swelling dissipates.
If you want to enjoy a more defined jawline and chin, both Kybella injections and chin liposuction are options. Visit a facial plastic surgeon that offers double chin reduction to discuss which treatment will be best for slimming your face, neck and jawline.
Posted on behalf of:
Maurice M. Khosh, MD, FACS
580 Park Avenue, Suite 1BE
New York, NY 10065
212-339-9988
The information provided on this website, including text, graphics, images, and other materials, is intended solely for informational purposes and should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.


)